
Cheyletiella Mites Humans Symptoms
Cheyletiella mites are tiny, parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals. They are commonly known as "walking dandruff" because they can be seen moving on the skin. In humans, cheyletiella mites typically cause a skin condition called cheyletiellosis, which is characterized by intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
Cheyletiellosis is most commonly spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. The mites can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing or bedding. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis typically develop within a few days of exposure to the mites.
Treatment for cheyletiellosis typically involves the use of topical or oral medications to kill the mites. It is also important to treat any infested animals to prevent the mites from re-infesting humans.
Cheyletiella Mites Humans Symptoms
Cheyletiella mites are tiny, parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals. They are commonly known as "walking dandruff" because they can be seen moving on the skin. In humans, cheyletiella mites typically cause a skin condition called cheyletiellosis, which is characterized by intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
- Cause: Cheyletiella mites are spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits.
- Symptoms: Cheyletiellosis causes intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
- Treatment: Treatment for cheyletiellosis typically involves the use of topical or oral medications to kill the mites.
- Prevention: Cheyletiellosis can be prevented by avoiding contact with infested animals and by washing hands frequently.
- Diagnosis: Cheyletiellosis is diagnosed by a doctor or veterinarian based on the symptoms and a physical examination.
- Prognosis: Cheyletiellosis is a treatable condition, and most people recover completely within a few weeks.
- Complications: In some cases, cheyletiellosis can lead to secondary infections.
- Epidemiology: Cheyletiellosis is a relatively common skin condition, especially in children and people who own pets.
- Research: There is ongoing research into new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis.
Cheyletiella mites are a common cause of skin irritation in humans. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can be distressing, but the condition is treatable and most people recover completely within a few weeks. If you think you may have cheyletiellosis, it is important to see a doctor or veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Cause
Cheyletiella mites are tiny, parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals. They are commonly known as "walking dandruff" because they can be seen moving on the skin. In humans, cheyletiella mites typically cause a skin condition called cheyletiellosis, which is characterized by intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
Cheyletiella mites are spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. The mites can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing or bedding. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis typically develop within a few days of exposure to the mites.
It is important to understand the cause of cheyletiellosis in order to prevent the condition. If you have a cat or rabbit, it is important to keep the animal clean and free of mites. You should also wash your hands frequently after handling your pet. If you think you may have cheyletiellosis, it is important to see a doctor or veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin. In some cases, cheyletiellosis can also cause a burning or stinging sensation.
- Itching: The itching associated with cheyletiellosis is often severe and can be very difficult to control. The itching is caused by the mites burrowing into the skin and feeding on the host's blood.
- Redness: The redness associated with cheyletiellosis is caused by the inflammation of the skin. The inflammation is a response to the mites burrowing into the skin and feeding on the host's blood.
- Small, red bumps: The small, red bumps associated with cheyletiellosis are caused by the mites burrowing into the skin and laying eggs. The eggs hatch into larvae, which then burrow into the skin and begin to feed on the host's blood.
Cheyletiellosis is a treatable condition, but it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. Treatment for cheyletiellosis typically involves the use of topical or oral medications to kill the mites.
Treatment
Cheyletiella mites are tiny, parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals. They are commonly known as "walking dandruff" because they can be seen moving on the skin. In humans, cheyletiella mites typically cause a skin condition called cheyletiellosis, which is characterized by intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
The treatment for cheyletiellosis typically involves the use of topical or oral medications to kill the mites. Topical medications are applied directly to the skin, while oral medications are taken by mouth. Both types of medication work by killing the mites and their eggs.
It is important to treat cheyletiellosis as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. If left untreated, cheyletiellosis can lead to a number of complications, including secondary skin infections and scarring.
In addition to treating the infested person, it is also important to treat any infested animals in the household. This will help to prevent the mites from re-infesting the person.
Prevention
Cheyletiella mites are tiny, parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals. They are commonly known as "walking dandruff" because they can be seen moving on the skin. In humans, cheyletiella mites typically cause a skin condition called cheyletiellosis, which is characterized by intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
Cheyletiellosis is most commonly spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. The mites can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing or bedding. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis typically develop within a few days of exposure to the mites.
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent cheyletiellosis, including:
- Avoiding contact with infested animals: The most effective way to prevent cheyletiellosis is to avoid contact with infested animals. This includes avoiding contact with stray animals, as well as animals that are known to be infested with mites.
- Washing hands frequently: Washing hands frequently with soap and water can help to remove cheyletiella mites from the skin. This is especially important after coming into contact with an infested animal.
- Keeping pets clean and free of mites: If you have a pet, it is important to keep it clean and free of mites. This can be done by bathing your pet regularly and using a flea and tick shampoo.
By following these simple tips, you can help to prevent cheyletiellosis and keep your skin healthy.
Diagnosis
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The diagnosis of cheyletiellosis is based on the symptoms and a physical examination. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of cheyletiellosis are the most important factor in diagnosing the condition. The doctor or veterinarian will ask about the patient's symptoms, including when they started, how severe they are, and if they have been getting worse.
- Physical examination: The doctor or veterinarian will also perform a physical examination to look for signs of cheyletiellosis. The doctor or veterinarian will look for small, red bumps on the skin, as well as any other signs of inflammation.
- Microscopic examination: In some cases, the doctor or veterinarian may also perform a microscopic examination of the skin to look for cheyletiella mites or their eggs.
By taking into account the patient's symptoms and the results of the physical and microscopic examinations, the doctor or veterinarian can diagnose cheyletiellosis.
Prognosis
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
The prognosis for cheyletiellosis is generally good. Most people recover completely within a few weeks of treatment. However, in some cases, the condition can be more difficult to treat and may require longer treatment.
- Factors that affect the prognosis of cheyletiellosis include:
- The severity of the infestation
- The patient's overall health
- The type of treatment used
- Treatment for cheyletiellosis typically involves the use of topical or oral medications to kill the mites.
- Topical medications are applied directly to the skin, while oral medications are taken by mouth.
- Both types of medication work by killing the mites and their eggs.
- In addition to treating the infested person, it is also important to treat any infested animals in the household.
- This will help to prevent the mites from re-infesting the person.
- Pets can be treated with topical or oral medications, or with special shampoos that kill mites.
- With proper treatment, most people with cheyletiellosis recover completely within a few weeks.
- However, in some cases, the condition can be more difficult to treat and may require longer treatment.
- If you have cheyletiellosis, it is important to see a doctor or veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Cheyletiellosis is a treatable condition, but it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. If left untreated, cheyletiellosis can lead to a number of complications, including secondary skin infections and scarring.
Complications
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
In some cases, cheyletiellosis can lead to secondary infections. This is because the mites can create small breaks in the skin, which can allow bacteria and other microorganisms to enter. Secondary infections can be more serious than cheyletiellosis itself, and they can lead to scarring or other complications.
There are a number of things that can increase the risk of developing secondary infections from cheyletiellosis, including:
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis
- Not treating cheyletiellosis promptly
If you have cheyletiellosis, it is important to see a doctor or veterinarian as soon as possible to get treatment. This will help to reduce the risk of developing secondary infections.
Epidemiology
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin. Cheyletiellosis is a relatively common skin condition, especially in children and people who own pets.
There are a number of reasons why cheyletiellosis is more common in children and people who own pets. Children are more likely to come into contact with animals that may be infested with cheyletiella mites. They are also more likely to play in areas where these mites may be present, such as in parks or petting zoos. People who own pets are also more likely to come into contact with cheyletiella mites, as these mites can be spread from animals to humans.
Understanding the epidemiology of cheyletiellosis is important for a number of reasons. First, it can help to identify populations that are at high risk for developing the condition. This information can be used to develop targeted prevention and control measures.
Research
Cheyletiellosis is a skin condition caused by cheyletiella mites. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin. Cheyletiellosis is a relatively common skin condition, especially in children and people who own pets.
The current treatments for cheyletiellosis are effective, but they can have side effects. For example, topical treatments can cause skin irritation, and oral medications can cause liver damage. Therefore, there is a need for new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis that have fewer side effects.
Ongoing research is focused on developing new topical and oral medications for cheyletiellosis. These new medications are designed to be more effective and have fewer side effects than the current treatments. In addition, researchers are also developing new methods for diagnosing cheyletiellosis, which will help to improve the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
The development of new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis is important for a number of reasons. First, it will help to improve the quality of life for people who suffer from this condition. Second, it will help to reduce the risk of developing complications from cheyletiellosis, such as secondary skin infections and scarring. Third, it will help to reduce the cost of treating cheyletiellosis.
FAQs on Cheyletiella Mites in Humans
Cheyletiella mites are tiny parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals, causing a skin condition called cheyletiellosis. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis include intense itching, redness, and small, red bumps on the skin. Here are some frequently asked questions about cheyletiella mites in humans:
Question 1: How are cheyletiella mites spread?
Cheyletiella mites are most commonly spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. The mites can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing or bedding.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of cheyletiellosis?
The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can vary depending on the severity of the infestation, but they typically include intense itching, redness, and the appearance of small, red bumps on the skin.
Question 3: How is cheyletiellosis diagnosed?
Cheyletiellosis is diagnosed based on the symptoms and a physical examination. A doctor or veterinarian may also perform a microscopic examination of the skin to look for cheyletiella mites or their eggs.
Question 4: How is cheyletiellosis treated?
Cheyletiellosis is typically treated with topical or oral medications to kill the mites. In addition to treating the infested person, it is also important to treat any infested animals in the household to prevent re-infestation.
Question 5: What are the complications of cheyletiellosis?
In some cases, cheyletiellosis can lead to secondary skin infections. This is because the mites can create small breaks in the skin, which can allow bacteria and other microorganisms to enter.
Question 6: How can cheyletiellosis be prevented?
Cheyletiellosis can be prevented by avoiding contact with infested animals and by washing hands frequently. It is also important to keep pets clean and free of mites.
Cheyletiellosis is a treatable condition, but it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. If you have any questions about cheyletiellosis, please consult with a doctor or veterinarian.
Tips for Preventing and Treating Cheyletiella Mites in Humans
Cheyletiella mites are tiny parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals, causing a skin condition called cheyletiellosis. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis include intense itching, redness, and small, red bumps on the skin. Here are some tips for preventing and treating cheyletiella mites in humans:
Tip 1: Avoid contact with infested animals. Cheyletiella mites are most commonly spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. Avoid contact with stray animals, and keep your pets clean and free of mites.
Tip 2: Wash your hands frequently. Cheyletiella mites can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing or bedding. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coming into contact with animals or their bedding.
Tip 3: Treat infested animals promptly. If you have a pet that is infested with cheyletiella mites, treat it promptly to prevent the mites from spreading to humans. There are a number of topical and oral medications available to treat cheyletiella mites in animals.
Tip 4: Vacuum your home regularly. Cheyletiella mites can live in carpets and furniture. Vacuum your home regularly to remove any mites or eggs that may be present.
Tip 5: Wash your bedding in hot water. Cheyletiella mites can also live in bedding. Wash your bedding in hot water to kill any mites or eggs that may be present.
Tip 6: See a doctor if you have symptoms of cheyletiellosis. If you have symptoms of cheyletiellosis, such as intense itching, redness, and small, red bumps on the skin, see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Cheyletiellosis is a treatable condition, but it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent and treat cheyletiella mites in humans.
Conclusion
Cheyletiella mites are tiny parasitic mites that can infest humans and animals, causing a skin condition called cheyletiellosis. Symptoms of cheyletiellosis include intense itching, redness, and small, red bumps on the skin. Cheyletiella mites are most commonly spread through contact with infested animals, such as cats or rabbits. The condition is treatable with topical or oral medications, but it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening.
Cheyletiella mites are a common cause of skin irritation in humans. The symptoms of cheyletiellosis can be distressing, but the condition is treatable and most people recover completely within a few weeks. If you think you may have cheyletiellosis, it is important to see a doctor or veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Discoveries And Insights Unveiled: Mark Levin's Illness, Unraveled
Uncovering Untold Truths: "Rachel Sharp On Luke Perry Death"
Unveiling Traylor Howard's Relationships: Surprising Discoveries
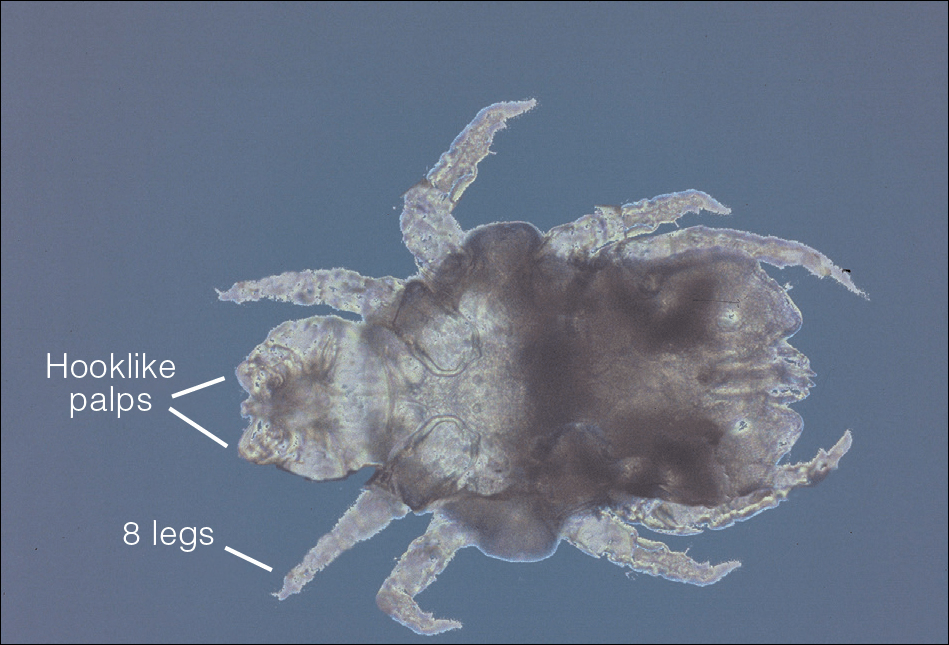

What’s Eating You? Cheyletiella Mites MDedge Dermatology
Dandruff Mites On Humans Toxoplasmosis My XXX Hot Girl

Figure 2
ncG1vNJzZmiblau%2FsLjLnqtnq2NjwrR51p6qrWViY66urdmopZqvo2OwsLmOnJ%2BesZyawaqxy6WYZqWZqbK0eceupJqmo2LAurnPraamq16dwa64